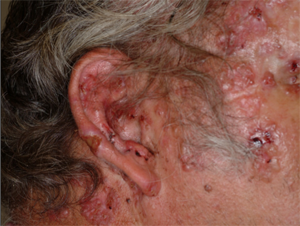
Basal cell carcinomas on the face of a person with Gorlin syndrome.
BCCs are a common symptom of the disease.
Also known as basal cell skin cancer, basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) is the most common feature of Gorlin syndrome. About 90% of people with Gorlin syndrome will have one or more BCCs by the age of 35.
BCCs happen when the cells in the bottom layer of the skin (the basal layer) become cancerous. Most basal cell cancers occur on skin that is regularly exposed to sunlight or other ultraviolet light radiation such as what is generated by tanning beds and certain types of lasers. In people with Gorlin syndrome, BCCs can develop in areas of the body that have not been exposed to much sunlight.
Basal cell carcinomas have raised borders that can appear glossy and shiny. BCCs can also be pink, red or skin-colored, and may have darker flecks in them and be dome-shaped, flat, bumpy or scaly. Some BCCs develop a small crater in the center, ooze or bleed easily and crust over.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer in the US. One in five Americans (without Gorlin syndrome) will develop a BCC. This type of BCC is called sporadic basal cell carcinoma.
Treatment for BCCs depends on the size, depth and location of the BCCs on the body, the patient’s age and health status. BCC treatment is typically managed by a dermatologist.
A basal cell carcinoma can be classified into subtypes. “Superficial” is the least invasive type of BCC. The other BCC types include nodular, sclerosing and morpheaform, which is the most aggressive. A biopsy and pathology report are the only definitive way to know the subtype.
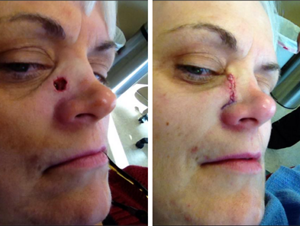
For more advanced BCCs, surgery may be required.
Knowing the BCC subtype is important to determining treatment. Because a person with Gorlin syndrome is likely to undergo multiple treatments for BCCs over his or her lifetime, the treatment approach is necessarily different than that of the “typical” skin cancer patient who may only undergo one or two surgeries.
There are several different types of treatments for basal cell carcinomas. These include surgery, topical treatments and oral medications. Surgery for BCCs are typically “outpatient” done in the provider’s office with local anesthesia. The patient returns home that day.
Treatments for basal cell carcinomas include:
Mohs surgery removes a thin layer of the BCC tissue. This layer is analyzed for cancer cells while the patient waits. If there is presence of cancer cells, the Mohs surgeon removes another layer for analysis. Once a layer is free of cancer cells, the wound is closed and the surgery is complete.
Excisional surgery is the removal of the entire BCC growth and some skin around it for a safety margin. The incision area is closed with stitches and the growth is sent to the lab for analysis.
Curettage and electrodesiccation, where the BCC growth is first removed with a special tool and then the area underneath is dessicated, or burned, with a fine needle used specifically for this purpose.
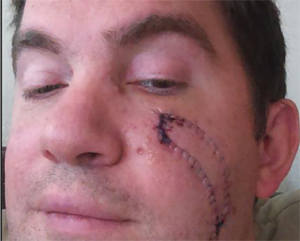
BCC surgery is usually an outpatient procedure.
Cryosurgery destroys the BCC growth by freezing it. Liquid nitrogen is applied directly to the BCC causing the growth to blister, scab over and eventually fall off.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) destroys BCCs by zapping them with a strong blue light after a topical “activating” agent is applied. Sunlight must be avoided for at least 48 hours after the procedure. PDT is used for superficial (thin BCCs) as it not effective on large or raised (nodular) BCCs. Photodynamic therapy is safer for people with Gorlin syndrome as it does not contain radiation.
Laser surgery, while not yet approved by the FDA for the treatment of superficial BCCs, uses a strong beam of light (the laser) to destroy BCCs.
Topical medications (imiquimod or 5 flurouracil) are applied to the tumor site multiple times of day for up to six weeks, depending on the type of medication.
Oral medications sonidegib (Odomzo) and vismodegib (Erivedge) are used for advanced cases of BCCs, adults with multiple BCCs, and those that are metastatic (spread to other parts of the body). Both cause severe birth defects and women must take caution to avoid pregnancy while on these medications. They cannot be used in children due to the risk of impaired bone growth.